
Director of Client Engagement
Organizations are racing to modernize and secure their networks and workforces. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) is an attractive framework for converging networking and security into a single solution. But as threats evolve,,,,, so does SASE and it is not surprising that we’re now entering AI driven, identity centric SASE. This is being referred to as “SASE 2.0.”
Past and even some present SASE deployments often meant blending SD-WAN and cloud security from multiple vendors. What we are seeing with suppliers is the next phase is all about AI and proactive continuous monitoring and response. AI and ML are becoming native to modern SASE platforms. This isn’t just about threat detection. We’re seeing SASE platforms that use AI to:
- Predict and prevent breaches
- Automate incident response
- Prioritize critical business traffic
- Self-heal network performance issues
This is creating a shift from reactive management to proactive infrastructure.
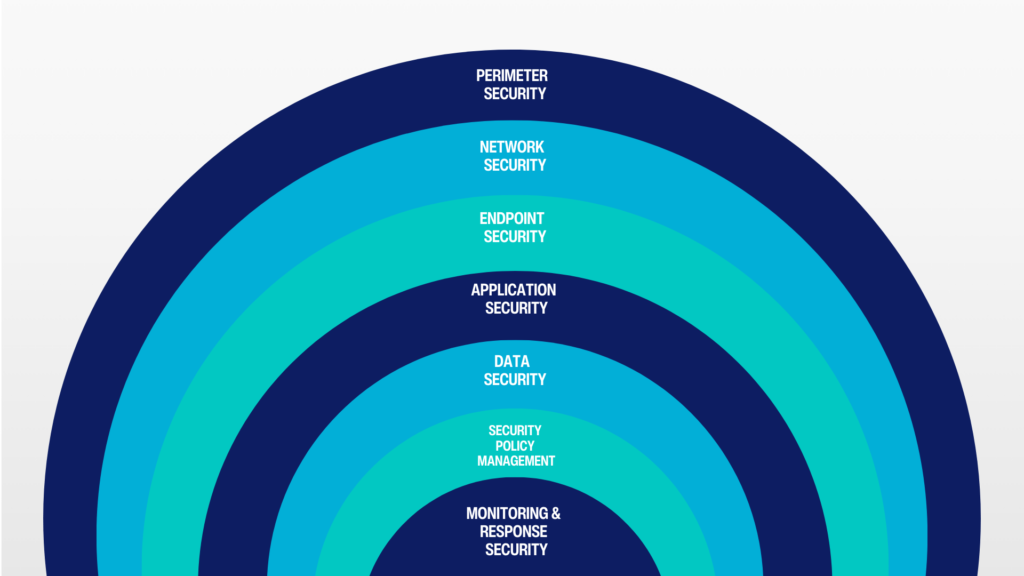
Under the SASE 2.0 framework, legacy and static firewalls are no longer enough. SASE 2.0 uses real time identity, device posture, user behavior, and location data to make access decisions. This new thought process of context aware, Zero Trust approach ensures that access is dynamic and not a “one size fits all”.
So, what’s the difference between ZTNA and ZTNA 2.0:
| Feature | ZTNA | ZTNA 2.0 |
| Access granularity | Per application | Per application + activity within apps |
| Trust evaluation | At login | Continuous and context-aware |
| Threat prevention | Minimal | Built-in and ongoing |
| Device context awareness | Limited | Required and dynamic |
The next evolution of SASE isn’t just about merging security and networking, it’s about making them intelligent, proactive and adaptive. Understanding where SASE is headed can help future proof your architecture.
If you’re exploring how to adapt your architecture to meet the demands of SASE 2.0 and beyond, our team at Technology Navigation is here to help. We work closely with organizations to cut through the noise, evaluate the right-fit solutions, and build secure, future-ready infrastructures. Let’s talk about how you can take a smarter, more strategic approach to networking and security. Reach out to start the conversation.